In today’s dynamic workplace environment, shift swapping protocols have become essential components of effective scheduling optimization strategies. Organizations across various industries are increasingly adopting flexible scheduling approaches to accommodate employee needs while maintaining operational efficiency. Shift swapping—the practice of employees trading scheduled shifts with qualified colleagues—offers a powerful solution that balances staff preferences with business requirements, particularly when implemented through modern mobile and digital scheduling tools.
The rise of digital workforce management has transformed how businesses handle shift exchanges, moving from manual, paper-based processes to sophisticated mobile platforms that streamline approvals, ensure compliance, and maintain appropriate staffing levels. When properly implemented, these systems empower employees while giving managers visibility and control over schedule changes. According to recent industry data, organizations implementing structured shift swapping protocols report significant improvements in employee satisfaction, reduced absenteeism, and decreased administrative burden on management teams.
Understanding Shift Swapping Fundamentals
Shift swapping represents a fundamental aspect of employee scheduling flexibility, allowing workers to trade assigned shifts when personal circumstances necessitate schedule adjustments. Rather than calling out or requesting last-minute schedule changes from management, employees can proactively find qualified colleagues to cover their shifts, creating a win-win scenario for staff and organizations alike.
- Definition and Purpose: Shift swapping is a structured process enabling employees to exchange scheduled work periods with qualified colleagues, maintaining coverage while accommodating personal needs.
- Evolution of Shift Trading: From informal agreements to sophisticated digital platforms with built-in approval workflows and compliance checks.
- Types of Shift Exchanges: Including direct swaps (trading shifts between two employees), open shift offerings (relinquishing a shift for anyone qualified to claim), and partial shift exchanges.
- Core Components: Effective protocols include request submission, qualification verification, management approval, notification systems, and documentation.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Encompasses employees initiating and accepting swaps, managers approving changes, and HR/compliance teams ensuring policy adherence.
Well-designed shift swapping systems provide structure while eliminating unnecessary friction, allowing employees to resolve scheduling conflicts without extensive management intervention. This approach aligns with modern workforce expectations for greater autonomy and work-life balance, especially among younger employees who prioritize scheduling flexibility in their employment decisions. Effective shift swapping represents a critical tool for organizations seeking to enhance employee experience while maintaining operational standards.
Benefits of Implementing Robust Shift Swapping Protocols
Organizations implementing well-structured shift swapping protocols through digital tools realize significant advantages across multiple business dimensions. From operational efficiencies to enhanced employee experience metrics, these systems deliver measurable returns on investment while supporting organizational agility in adapting to changing conditions.
- Increased Employee Satisfaction: Employees gain greater control over their schedules, improving work-life balance and job satisfaction while reducing burnout risk.
- Reduced Absenteeism: Properly managed shift swaps decrease last-minute call-outs by providing alternatives when personal conflicts arise with scheduled shifts.
- Enhanced Productivity: Staff working preferred shifts typically demonstrate higher engagement and productivity levels compared to those working unwanted schedules.
- Administrative Time Savings: Digital shift swapping systems reduce management time spent on schedule adjustments by up to 70% according to industry studies.
- Improved Retention Rates: Organizations offering flexible scheduling options including streamlined shift swapping report lower turnover rates, particularly in retail, hospitality, and healthcare sectors.
Research indicates that businesses implementing structured shift marketplace solutions see measurable improvements in key performance indicators, including increased employee retention and reduced overtime costs. By empowering employees to resolve scheduling conflicts collaboratively, organizations create more resilient workforces while minimizing disruptions to operations. Additionally, these systems generate valuable data on scheduling patterns and employee preferences that can inform future workforce planning decisions.
Common Challenges in Shift Swapping Management
Despite their benefits, shift swapping initiatives frequently encounter obstacles that can undermine effectiveness if not properly addressed. Understanding these challenges is crucial for designing systems that deliver optimal results while mitigating potential risks to operations, compliance, and team dynamics.
- Qualification Mismatches: Ensuring employees trading shifts possess equivalent skills, certifications, and authorizations to perform required duties without compromising service quality or safety.
- Compliance Violations: Managing shift swaps that could potentially create overtime situations, break hour and rest period violations, or conflicts with labor regulations and union agreements.
- Communication Breakdowns: Preventing miscommunications about approved swaps that lead to coverage gaps, double-staffing, or confusion about shift responsibilities.
- Approval Bottlenecks: Avoiding delays in the approval process that can frustrate employees and reduce the effectiveness of the shift swapping system.
- Fairness Concerns: Addressing perceptions of favoritism or unequal access to desirable shifts that can emerge without transparent protocols.
Organizations must also consider the impact of shift swapping on team cohesion and departmental knowledge continuity. Excessive shift changes can disrupt team dynamics and information flow, particularly in collaborative environments. Managing shift changes effectively requires balancing flexibility with operational stability. Implementing digital solutions with built-in rule enforcement, clear approval workflows, and transparent processes helps mitigate these challenges while maintaining the benefits of flexible scheduling.
Essential Components of Effective Shift Swapping Systems
Successful shift swapping protocols incorporate several key elements that ensure smooth operations while protecting both employee and organizational interests. These components work together to create a balanced system that offers flexibility without compromising operational requirements or compliance standards.
- Clear Eligibility Guidelines: Defined parameters for who can swap shifts with whom, based on roles, skill sets, certifications, and training requirements.
- Streamlined Request Process: Simple, accessible mechanisms for initiating, viewing, and accepting shift swap opportunities through mobile or web-based platforms.
- Automated Compliance Checks: System validation against labor laws, overtime thresholds, required rest periods, and organizational policies before approvals.
- Transparent Approval Workflows: Clear processes specifying who must approve swaps, approval criteria, and expected response timeframes.
- Comprehensive Notification Systems: Automated alerts to all affected parties about swap requests, approvals, denials, and schedule updates.
- Audit Trails and Documentation: Complete records of all swap requests, approvals, and resulting schedule changes for compliance and analysis purposes.
Organizations should develop protocols that balance employee autonomy with appropriate oversight. Team communication is essential throughout the shift swapping process, ensuring all stakeholders remain informed about schedule changes. Modern mobile technology platforms like Shyft facilitate this communication while streamlining the swap process, making it easier for employees to find qualified colleagues available to take their shifts.
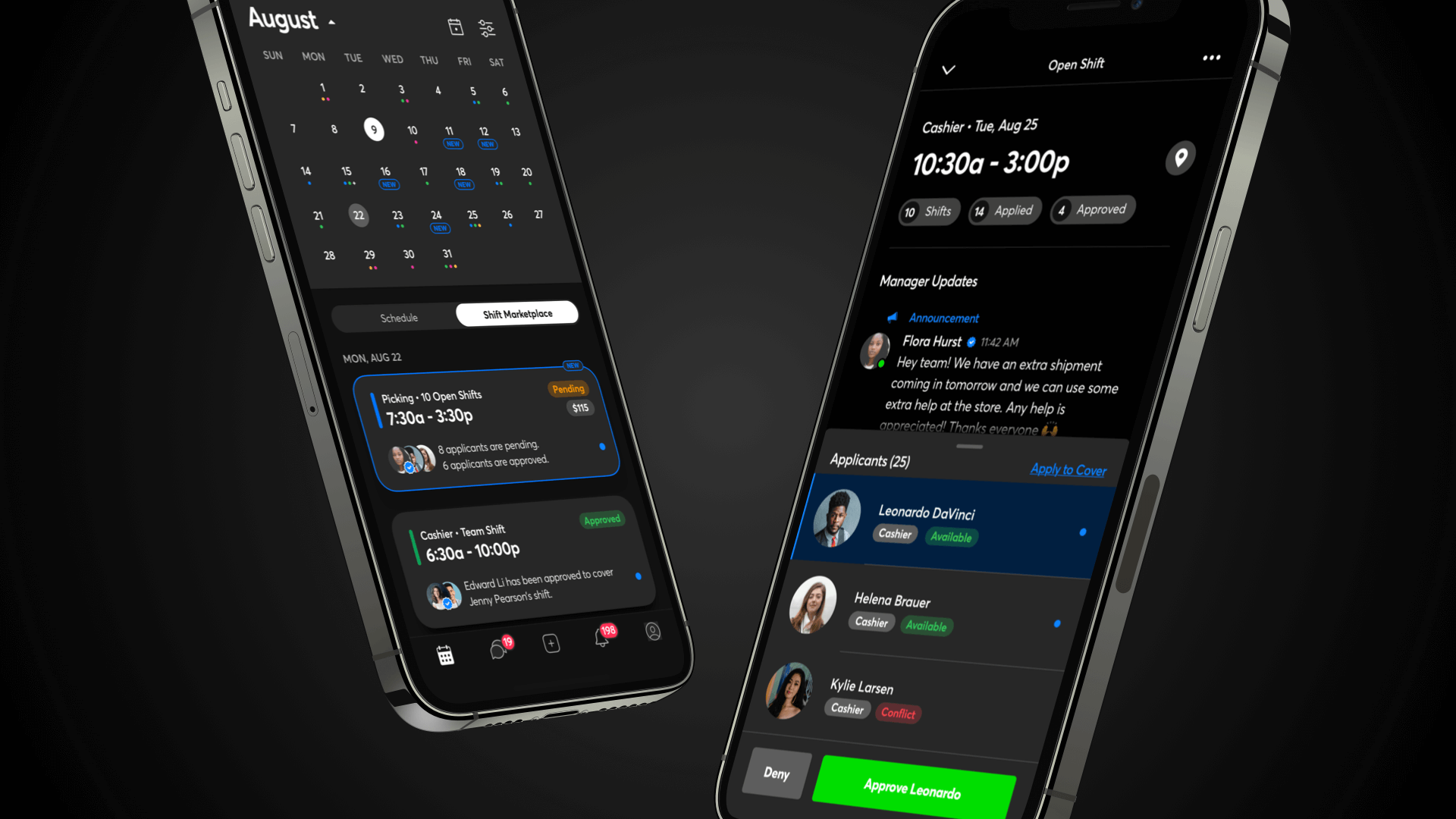
Leveraging Mobile Technology for Shift Swapping
Mobile applications have revolutionized shift swapping capabilities, transforming what was once a cumbersome manual process into a streamlined digital experience. These platforms connect employees directly, facilitate rapid communication, and automate compliance checks, dramatically improving the efficiency of workforce scheduling adjustments.
- Real-Time Availability Updates: Mobile platforms display current shift openings and employee availability instantly, facilitating faster matches between shift needs and willing workers.
- Push Notification Capabilities: Immediate alerts about swap opportunities, requests, approvals, or denials keep all parties informed throughout the process.
- Location-Independent Access: Employees can manage shift swaps from anywhere, eliminating the need to be on-site to arrange schedule changes.
- Digital Marketplace Features: Advanced platforms create internal marketplaces where employees can post and claim shifts based on qualifications and preferences.
- Integration Capabilities: Connections with timekeeping, payroll, and HRIS systems ensure schedule changes are properly documented and reflected in related systems.
Solutions like Shyft’s platform leverage mobile technology to create intuitive experiences for both employees and managers. These tools typically include built-in messaging capabilities that facilitate direct communication between team members regarding potential swaps while maintaining appropriate privacy boundaries. The real-time notifications feature ensures all stakeholders stay informed about schedule changes, reducing confusion and preventing coverage gaps.
Compliance Considerations in Shift Swapping
Maintaining regulatory compliance while facilitating shift flexibility presents significant challenges for organizations. Various laws, regulations, and contractual obligations affect how shifts can be traded, necessitating careful attention to compliance factors in shift swapping protocols.
- Overtime Management: Systems must monitor how shift swaps affect weekly hours to prevent inadvertent overtime situations that could violate labor laws or budget constraints.
- Required Rest Periods: Protocols should enforce mandatory rest periods between shifts as required by regulations, preventing employees from accepting swaps that would violate these requirements.
- Minor Work Restrictions: Special considerations for employees under 18, including limitations on hours, shift times, and job duties that may restrict swap eligibility.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Sector-specific requirements such as nurse-to-patient ratios in healthcare or safety-sensitive position requirements in transportation.
- Union Agreement Compliance: Adherence to collective bargaining provisions regarding seniority, shift assignments, and scheduling procedures.
Labor compliance must remain a priority when implementing shift swapping protocols. Digital platforms can automate compliance checks, flagging potential violations before they occur. For example, systems can prevent swaps that would create shifts longer than permitted by law or that would violate required break periods. Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions face additional complexity, as they must account for varying regulations in different locations. Legal compliance features in scheduling software can help navigate these complexities by applying location-specific rules automatically.
Implementing a Shift Marketplace Approach
Advanced shift swapping protocols often incorporate marketplace concepts, creating internal platforms where employees can post, browse, and claim available shifts. This approach expands beyond simple one-to-one exchanges, offering greater flexibility while maintaining necessary controls.
- Open Shift Posting: Allows employees to relinquish shifts to a general pool where any qualified worker can claim them, expanding the pool of potential coverage.
- Skill-Based Matching: Automatically filters available shifts based on employee qualifications, certifications, and experience levels to ensure appropriate coverage.
- Incentive Integration: Some systems allow for premium pay or other incentives for taking hard-to-fill shifts, increasing participation in the marketplace.
- Preference-Based Algorithms: Advanced matching technology that considers employee location, time preferences, and career development needs when suggesting potential swaps.
- Cross-Department Opportunities: Enables qualified employees to pick up shifts across different departments or locations, maximizing workforce utilization.
The shift marketplace concept represents an evolution beyond basic swapping, creating an internal gig economy that benefits both employees and organizations. Platforms like Shyft Marketplace facilitate this approach by creating user-friendly interfaces where employees can easily view available opportunities aligned with their qualifications. This model is particularly effective in industries with variable demand patterns and diverse skill requirements, such as healthcare, retail, and hospitality.
Management Best Practices for Shift Swapping
While technology enables shift swapping, effective management practices remain essential for successful implementation. Leaders must establish clear guidelines, provide appropriate oversight, and foster a culture that balances flexibility with accountability.
- Documented Policy Development: Create comprehensive written policies defining eligibility, request procedures, approval criteria, and consequences for non-compliance.
- Tiered Approval Systems: Implement approval workflows that match the level of scrutiny to the potential impact, allowing routine swaps to proceed with minimal oversight while flagging higher-risk changes.
- Employee Training: Provide thorough instruction on using swap systems, understanding compliance requirements, and following protocols correctly.
- Regular Policy Reviews: Schedule periodic assessments of swap protocols to identify improvement opportunities and address emerging challenges.
- Data-Driven Adjustments: Analyze swap patterns to identify underlying scheduling issues, recurring conflicts, or opportunities to improve base schedules.
Managers should view shift swapping not just as an administrative process but as a strategic tool for enhancing workforce flexibility and employee satisfaction. Effective oversight includes monitoring patterns to identify potential issues while allowing employees appropriate autonomy. Organizations should consider implementing performance metrics for shift management that track the effectiveness of their swap protocols, including metrics like approval time, coverage rate, and employee satisfaction with the process.
Measuring Success: Shift Swap Metrics and KPIs
Evaluating the effectiveness of shift swapping protocols requires tracking key performance indicators that measure both operational impact and employee experience. These metrics help organizations refine their approaches and demonstrate return on investment for digital scheduling tools.
- Swap Request Volume: Track the number of swap requests to identify patterns, peak periods, and potential underlying scheduling issues.
- Fulfillment Rate: Measure the percentage of swap requests successfully filled, indicating system effectiveness in facilitating coverage.
- Response Time Metrics: Monitor average time for swap requests to receive responses from colleagues and management approvals.
- Compliance Violation Reduction: Track decreases in scheduling compliance issues such as inadvertent overtime or rest period violations.
- Administrative Time Savings: Quantify reduction in management hours spent handling schedule adjustments manually.
- Employee Satisfaction Scores: Measure improvements in scheduling-related satisfaction through targeted surveys and feedback mechanisms.
Organizations should establish baseline measurements before implementing new swap protocols, allowing for meaningful before-and-after comparisons. Workforce analytics capabilities in modern scheduling platforms provide valuable insights into swap patterns, helping identify opportunities for schedule optimization. For example, frequent swap requests for particular shifts might indicate underlying issues with the base schedule that could be addressed through adjustments to core scheduling practices.
Integration with Broader Scheduling Strategies
Shift swapping protocols work most effectively when integrated with comprehensive scheduling strategies that address workforce needs holistically. Organizations should view swap capabilities as one component of a broader approach to scheduling flexibility and workforce optimization.
- Preference-Based Scheduling: Combine swap capabilities with upfront collection of availability and preferences to create initial schedules that minimize the need for changes.
- Demand Forecasting Integration: Use historical data and predictive analytics to anticipate staffing needs more accurately, reducing last-minute coverage challenges.
- Cross-Training Initiatives: Develop employee skills across multiple roles to expand the pool of qualified workers able to cover various positions during swaps.
- Self-Scheduling Components: Implement partial self-scheduling where appropriate, allowing employees to select shifts from pre-approved options before manager-assigned scheduling.
- Flexible Staffing Models: Consider supplementing core staff with on-call, part-time, or flexible workers specifically available to cover scheduling gaps.
The most successful organizations view shift swapping as part of an integrated approach to schedule optimization rather than as an isolated process. By connecting swap protocols with other scheduling initiatives like employee preference data collection and workload forecasting, businesses can create more resilient and responsive scheduling systems. These integrated approaches minimize disruptions while maximizing both operational performance and employee satisfaction.
Future Trends in Shift Swapping Technology
The evolution of shift swapping protocols continues as new technologies emerge and workforce expectations evolve. Forward-thinking organizations should monitor these developments to stay ahead of the curve in scheduling flexibility and optimization.
- AI-Powered Matching Algorithms: Advanced artificial intelligence that learns from past swap patterns to suggest optimal matches based on multiple factors beyond basic qualifications.
- Predictive Analytics Integration: Systems that anticipate potential scheduling conflicts and proactively suggest swap opportunities before employees even request changes.
- Blockchain for Swap Verification: Distributed ledger technology providing transparent, tamper-proof records of shift trades and approvals.
- Voice-Activated Swap Requests: Integration with virtual assistants allowing employees to initiate and manage shift swaps through conversational interfaces.
- Gig Economy Platform Integration: Connections between internal swap systems and external workforce platforms to fill coverage gaps when internal resources are unavailable.
Emerging technologies like AI-enhanced shift swapping promise to make these systems even more effective by automating matching processes and providing deeper insights into scheduling patterns. As these technologies mature, organizations implementing them gain competitive advantages in workforce management efficiency and employee experience. The continued development of mobile platforms will further enhance accessibility and user experience, making shift swapping increasingly seamless for all stakeholders.
Conclusion
Effective shift swapping protocols represent a critical component of modern workforce management strategies, balancing operational requirements with employee needs for flexibility and work-life balance. When properly implemented through mobile and digital platforms, these systems deliver measurable benefits including increased employee satisfaction, reduced administrative burden, improved coverage reliability, and enhanced compliance with labor regulations. The key to success lies in designing protocols that provide appropriate structure and oversight while eliminating unnecessary friction in the process.
Organizations seeking to optimize their approach to shift swapping should evaluate their current practices against industry best practices, implement appropriate digital tools with built-in compliance features, and establish clear metrics to measure success. By viewing shift swapping as an integral component of comprehensive scheduling strategies rather than an isolated process, businesses can create more resilient workforces while improving operational outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, those who embrace innovative approaches to shift flexibility will gain significant advantages in employee retention, productivity, and overall workforce management effectiveness.
FAQ
1. What are the essential components of an effective shift swapping policy?
An effective shift swapping policy should include clear eligibility guidelines specifying who can swap with whom based on qualifications and roles, a streamlined request and approval process, automated compliance checks against labor laws and organizational policies, transparent approval workflows with defined timeframes, comprehensive notification systems for all affected parties, and complete documentation of all swap activities. The policy should balance employee flexibility with operational requirements and compliance considerations while minimizing administrative burden through appropriate automation.
2. How can organizations ensure compliance when implementing shift swapping protocols?
Organizations can ensure compliance by implementing digital tools with built-in rule enforcement that automatically checks potential swaps against relevant regulations, incorporating parameters for overtime thresholds, required rest periods, minor work restrictions, and qualifications verification. These systems should maintain comprehensive audit trails of all swap activities, apply location-specific rules for multi-jurisdiction operations, include manager review for high-risk swaps, provide regular compliance training for all users, and schedule periodic policy reviews to address evolving regulatory requirements.
3. What metrics should be tracked to evaluate shift swapping effectiveness?
Key metrics for evaluating shift swapping effectiveness include swap request volume (total number of requests over time), fulfillment rate (percentage of requests successfully filled), avera